


What if I told you that the way we approach healthcare is about to change forever? Hold your breath, because the tools you know are being overshadowed by a revolutionary force.
In today's fast-paced world, healthcare is a cornerstone of societal well-being. As technology evolves, innovative AI-powered solutions are disrupting the industry unlike anything before. Could traditional methods soon be obsolete?

Traditionally, diagnosing a disease required a plethora of tests and specialist consultations. Yet, what's surfacing now is redefining diagnosis completely. AI systems process data at lightning speed, identifying patterns the human eye might miss. But that's not even the wildest part…
Consider this: AI not only diagnoses but predicts health outcomes before symptoms manifest. Patients could soon know their future health risks without stepping inside a clinic. What could this mean for preventative medicine? But even experts weren't prepared for what follows…
Imagine a future where a simple device in your pocket could monitor your health in real-time, learning and adapting as it gathers data. This isn't science fiction—it's happening now. What happens next shocked even the experts…
Predictive analytics in healthcare is gaining momentum, offering insights into patient health before any symptoms arise. By analyzing a patient’s history and genetic data, AI predicts if diseases like cancer or diabetes might develop. This proactive approach could transform healthcare delivery. But there's one more twist...

AI-powered tools are not only diagnosing but also suggesting personalized treatments. Imagine algorithms tailored to the individual's lifestyle and genetic makeup, maximizing treatment effectiveness. It's a new era where AI becomes a co-pilot in patient care decisions. But there’s something you might never have considered…
The integration of AI with electronic health records provides clinicians immediate access to a wealth of patient data, speeding up decision-making processes. As a result, patient care becomes more efficient and precise, a stark contrast to the time-consuming processes of the past. Yet, the implications run deeper…
This innovation raises questions about privacy and ethics, making us rethink patient data security. As AI systems grow more powerful, how will they protect sensitive health information? What you read next might change how you see this forever.
Implementing AI in healthcare isn't without challenges. While advances offer benefits, they also come with hidden costs. The initial investment in AI systems can be steep, a barrier for smaller healthcare facilities. However, once integrated, their potential for cost-savings and improved patient outcomes can't be ignored.

A study found that AI could reduce healthcare costs by $150 billion by 2026 in various ways, including by reducing misdiagnoses and hospital admissions. This balance between cost and benefit leaves much to ponder. What else is hidden beneath the surface?
Despite the cost concerns, AI tools continually prove their worth. An automated image analysis, for instance, assists radiologists in identifying abnormalities far quicker than conventional methods. This reduces patient wait times and accelerates treatment plans. Yet, a bigger question looms...
Can these AI systems operate without the risk of malfunction, and who bears the liability if they fail? As healthcare increasingly embraces technology, understanding these hidden challenges becomes crucial. Discover the unforeseen impacts AI has on healthcare systems next…
AI is revolutionizing drug development, slashing years off the process. Algorithms analyze vast datasets, identifying potential drug candidates faster than traditional research methods. This acceleration means more treatments reach the market sooner, benefiting countless patients. But what about the unseen factors at play?

AI's data-crunching capabilities uncover patterns and interactions within biological data, predicting effective compounds faster. This not only expedites treatments but also reduces costs. However, there's another side to this coin…
As these methods evolve, so does the complexity of regulatory compliance. AI pushes traditional boundaries, requiring new frameworks to ensure safety and efficacy. Navigating this evolving landscape is essential for future innovation. But what comes next might astonish you...
The promise of AI-driven drug discovery brings hope, yet it also poses ethical questions about intellectual property and data ownership in pharmaceutical research. As we explore these challenges, we uncover even more surprising revelations…
Once a concept of the future, robotic surgery is now a lifesaving reality. Robots assist surgeons with unparalleled precision, minimizing human error and lowering recovery times. But their potential extends even further...
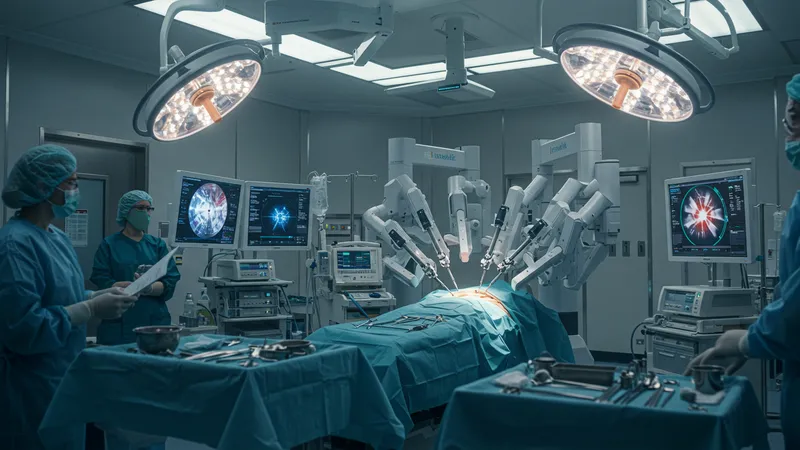
Robots equipped with AI assist in complex surgeries, making intricate maneuvers with absolute precision. As AI aids these machines, surgeries become less invasive and more predictable, increasing patient safety and comfort. Yet, there's a catch you might not expect…
While the benefits are apparent, the cost and availability of these technologies could widen the healthcare gap, creating disparities in patient access. Balancing innovation with equality remains a pressing challenge. What lies beyond this innovation brings more to question...
As robotic surgeries grow in popularity, understanding their financial and ethical implications is critical. How will insurance models adapt, and what role does AI play in this transition? The next innovation will take you by surprise…
Telemedicine has surged, offering convenience and access where it's needed most. Patients connect with healthcare professionals virtually, breaking traditional boundaries. But how did this become a game-changer amid the healthcare evolution?

Digital consults provide an alternative to in-person visits, making healthcare more accessible and reducing overhead costs. This transformative use of technology reshapes how we approach care delivery. But an even more intriguing perspective awaits...
The rise of telemedicine also sparks discussions about data security and patient privacy. As more interactions occur online, the demand for robust cybersecurity measures becomes paramount. How will this affect the future of healthcare communication?
Telehealth highlights the versatility of tech in modern healthcare, demonstrating we’re only scratching the surface of potential. The impact of seamless, remote interactions may change how we perceive healthcare access forever. Delving deeper, we uncover yet another layer of transformation…
As AI technologies advance, they bring ethical dilemmas that healthcare must address. The balance between technological prowess and humanity's moral compass faces constant scrutiny. What are the fundamental concerns surrounding AI ethics in healthcare?

Bias in AI algorithms poses significant risks, potentially perpetuating inequalities in patient care. Ensuring fairness in AI-driven outcomes requires vigilant oversight. Is technology neutral, or does it reflect human prejudices? Diving deeper reveals more about this controversy…
Patient consent and autonomy become blurred as AI integrates into decision-making. How much control should AI hold versus the human clinician? This intersection of autonomy and AI-driven advice remains a grey area in modern medicine. Could this change our understanding of patient rights?
The ethical landscape is as complex as the technology itself, challenging beliefs about healthcare delivery. With every advancement, the importance of ethical guidelines grows. What comes next in the evolution of AI ethics in medicine is a revelation worth exploring…
Personalized medicine is a beacon of hope in modern healthcare, driven by AI's capacity to tailor treatments to individual needs. What makes personalized treatments more effective than traditional methods?
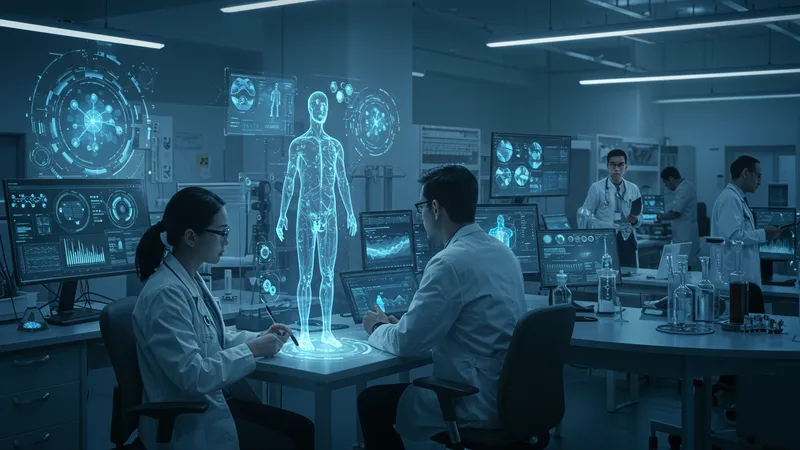
AI leverages patient data to customize therapies, enhancing precision in treatment and reducing adverse reactions. This approach revolutionizes care, offering targeted interventions with greater success. But there's more to this story...
Advancements in genomics, powered by AI, usher in the era of personalized medicine, where treatments are as unique as each patient. This precision easing healthcare burdens and improving outcomes leads to another transformative realization...
Personalized medicine challenges conventional standards, requiring a shift in both clinical training and healthcare policies. How will healthcare providers prepare for this change? Discover the future of personalized treatment strategies next…
AI-driven diagnostics are not just a concept; they are revolutionizing patient care. With AI, patients receive timely and accurate diagnoses, reshaping the future of diagnostics. But how does this translate in real-world applications?
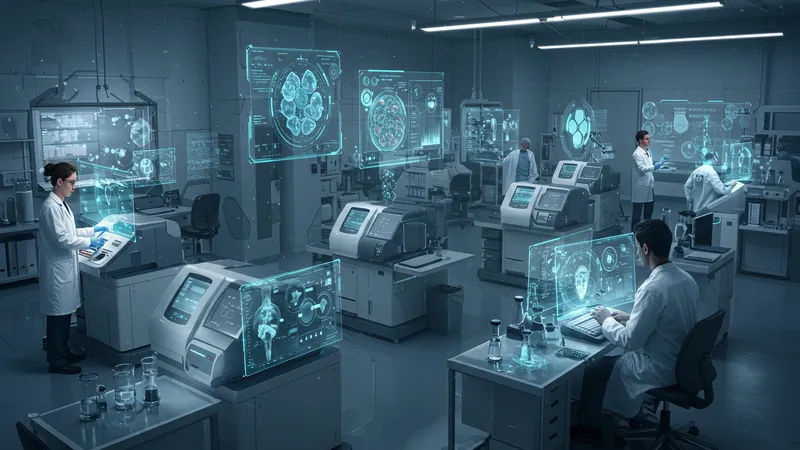

AI systems scan medical imaging faster, detecting anomalies that might elude the human eye. Hospital waiting times are reduced, and diagnostic accuracy improves drastically. But beneath this efficiency lies an unexpected finding...
As automation in diagnostics grows, the role of clinicians evolves, offering new challenges and opportunities. Will this shift streamline efficiencies or create dependency on technology? This dynamic change presents a broader impact yet to be explored...
The convergence of AI and diagnostics holds potential for early detection and prevention of diseases, paving the path toward future breakthroughs. How will this evolution influence patient experiences and outcomes? Further insights await eager exploration…
Beyond direct patient care, AI reshapes healthcare administration, optimizing operations and enhancing efficiencies. What does AI-inspired administration mean for healthcare facilities in practical terms?
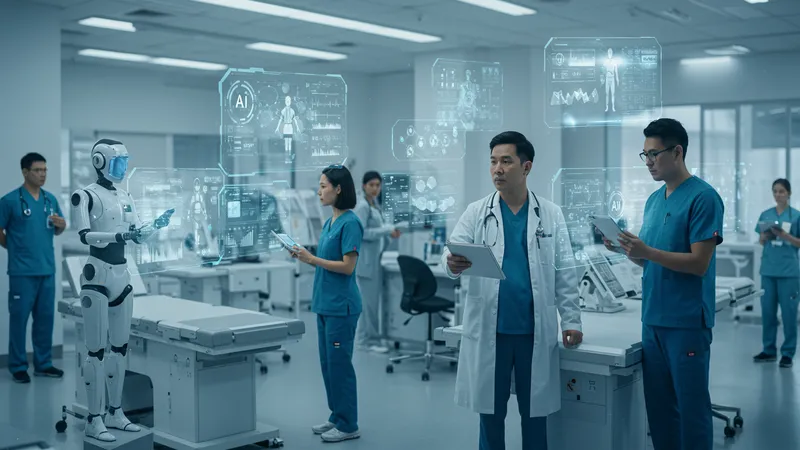

AI streamlines processes, from scheduling to resource allocation, minimizing human error and boosting productivity. Administrators find AI invaluable in managing day-to-day operations. But what surprises lurk behind AI's administrative facade?
The increased reliance on AI in administrative tasks sparks concerns over job losses and data security. Balancing technological benefits with potential downsides requires cautious consideration. Dive deeper to uncover AI's intricate role in administration…
As AI brings cost-effective solutions, understanding its impact on healthcare employment is crucial. How will roles adapt to integrate with AI workflows? This transformation is just beginning and offers real-world lessons worth noting…
AI's potential extends into mental health, providing new pathways for support and intervention. What role does AI play in transforming mental health care?
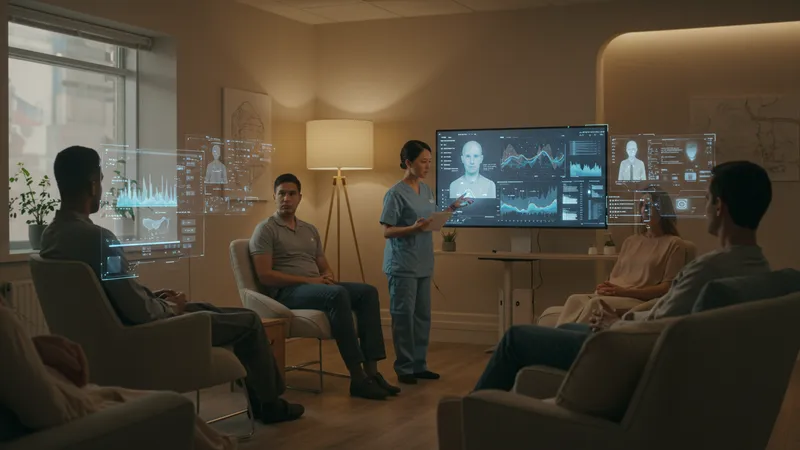

AI-driven platforms offer real-time monitoring and support, providing timely interventions for mental health issues. Chatbots and virtual therapists are breaking the stigma barrier. Yet, there is a deeper impact to consider…
AI solutions offer anonymity, encouraging individuals to seek help without fear of judgment. However, dependence on machines for emotional support raises questions about empathy's role in AI interactions. What truly defines a therapeutic relationship?
Exploring AI's integration in mental health unveils unprecedented possibilities, but ethical and professional implications linger. How ai technology coexists with traditional therapy requires careful exploration and adaptation. These insights reveal more concealed truths…
Incorporating sustainability into AI-powered healthcare technologies is becoming essential. How do AI innovations align with sustainable practices in healthcare?
AI tools reduce waste and optimize energy use in healthcare facilities, cutting emissions without compromising patient care. This alignment promises a greener future. But what are the hidden challenges?
Sustainable AI implementations require local regulations and resource allocations, presenting financial challenges for smaller systems. As the push for environmental responsibility grows, so does the call for equitable resource distribution. What more lies beneath this transformation?
The impact of AI on sustainability extends beyond individual facilities, setting a benchmark for global healthcare systems. How these innovations transcend environmental boundaries offers insights into future healthcare methodologies. This journey uncovers another interesting facet…
The next generation of healthcare professionals faces the challenge of integrating AI into practice. How should training programs adapt to this technological shift?

Emphasizing AI literacy, curriculums must include technology-focused modules. Healthcare education evolves to create practitioners fluent in both bedside manners and AI interfaces. But there's a broader impact to explore…
Rethinking traditional medical education involves collaboration between technologists and educators, bridging gaps between clinical expertise and algorithmic proficiency. AI's role in education paves the way for future innovations yet uncovered…
Preparing students for AI-enabled healthcare ensures a competent workforce, ready to harness the potential of AI while maintaining core medical ethics. What are the forthcoming challenges in evolving educational frameworks to include AI? Investigate deeper into this paradigm shift…
The journey through AI-powered healthcare illuminates both the potential and the complexity of integrating technology into human care. As we venture toward a digital health revolution, the balance between innovation and ethics grows paramount. Would you share this exploration with others, ensuring we adopt these insights wisely?